Introduction
Infrastructure teams waste hours answering repetitive questions like “How do I restart a Kubernetes pod?” or “Why is my database connection failing?” They also spend time manually creating JIRA tickets, copying details, and assigning them to the right team.
This blog shows how to build an AI-powered Slack bot that solves both problems: it searches a knowledge base using RAG (Retrieval-Augmented Generation) to answer questions instantly, or automatically creates JIRA tickets with smart team routing when it can’t find an answer. All running locally with Ollama—no cloud LLM costs.
How It Works
The bot follows a simple decision flow: search knowledge base first, create ticket if needed.
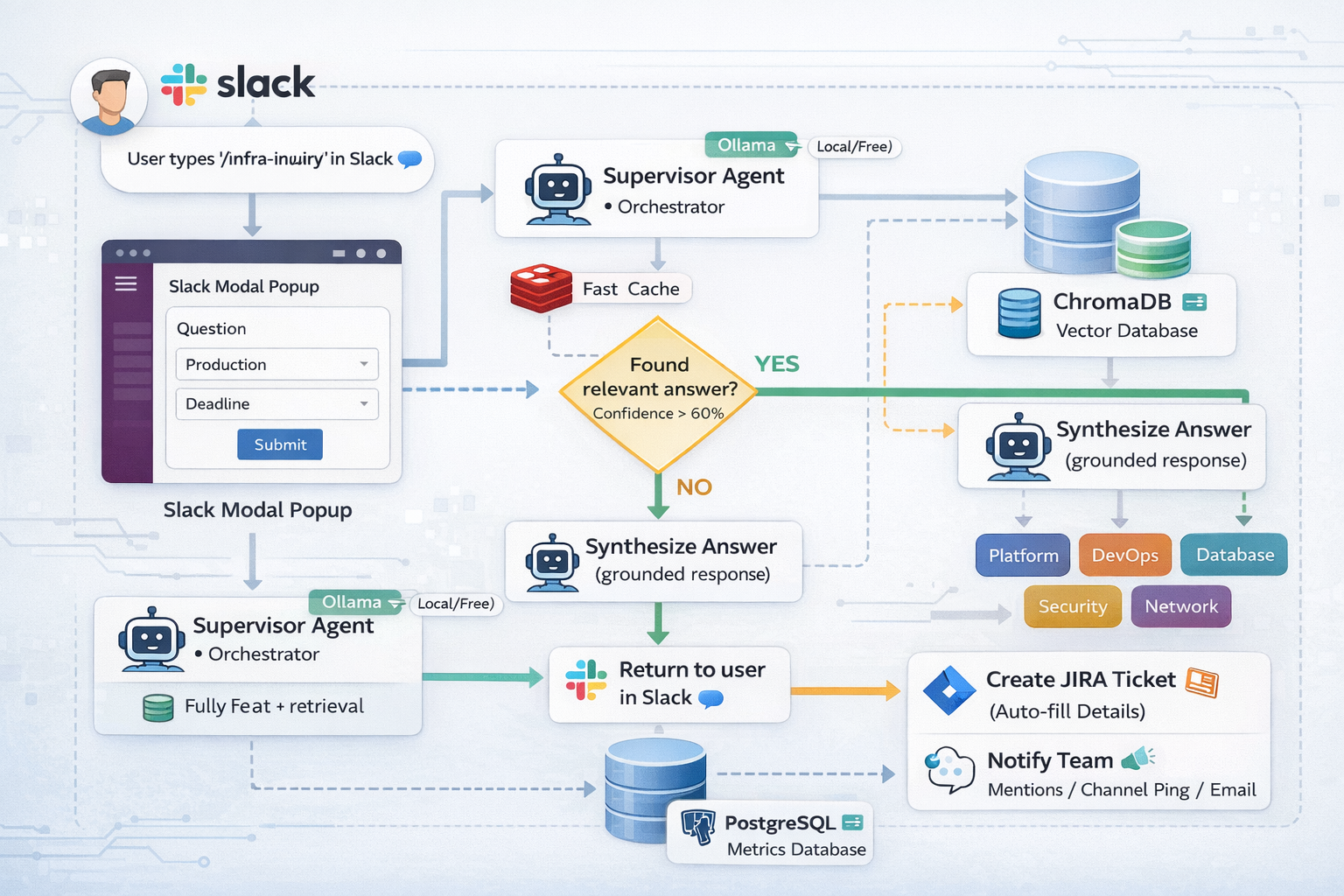
Components:
- Slack Bot - Captures questions via
/infra-inquirycommand - Ollama - Local LLM (
llama3.1:8b) for AI reasoning - ChromaDB - Vector database storing knowledge base
- PostgreSQL - Tracks all inquiries and metrics
- JIRA - Auto-creates tickets with team assignment
Using the Slack Command
When a user needs help, they type /infra-inquiry followed by their question. A modal appears asking for environment (PROD/STG/DEV) and deadline.
Output:
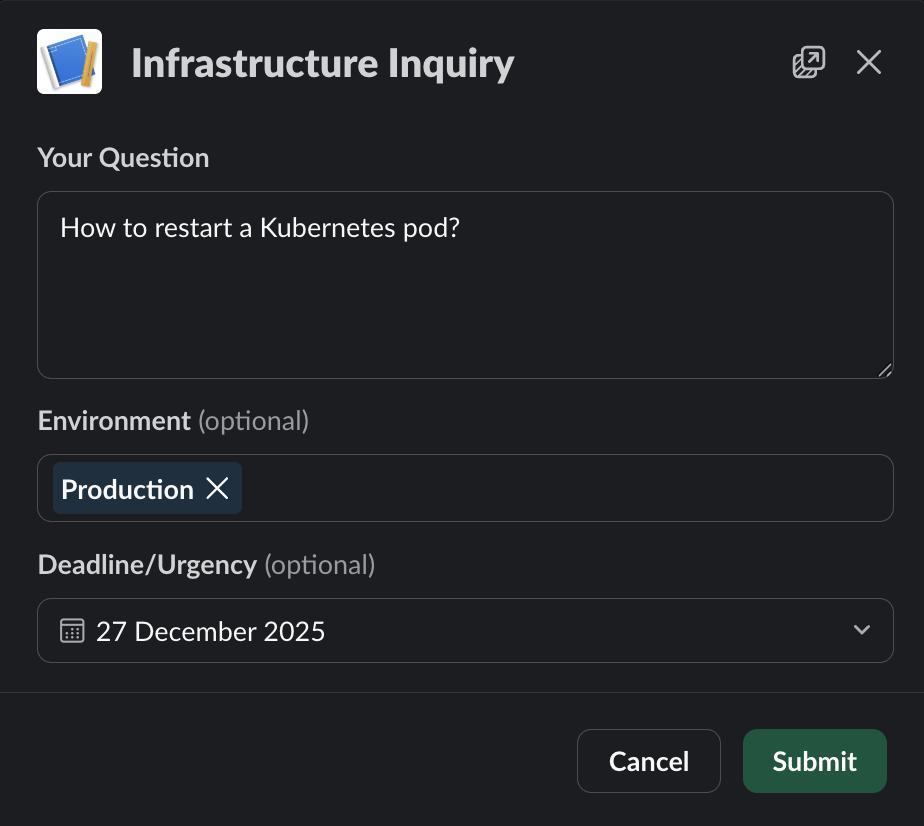
The modal captures context that helps the bot classify urgency and route tickets appropriately. RAG (Retrieval-Augmented Generation) combines AI with a searchable knowledge base to provide accurate answers without hallucinations.
Knowledge Base Search
The bot converts questions into vector embeddings (numerical representations) and searches ChromaDB for semantically similar Q&As. If confidence is high (>60%), it returns the answer immediately.
How it searches:
def search_knowledge(question):
# Convert question to vector embedding
embedding = create_embedding(question)
# Search ChromaDB for similar Q&As
results = chromadb.search(embedding, top_k=3)
# Check confidence threshold
if results.distance < 0.4: # High confidence match
return synthesize_answer(results)
return None # Not found, create ticket instead
What happens: The bot searches its knowledge base first. If it finds a relevant answer with high confidence, it responds instantly. Otherwise, it creates a ticket.
Output:
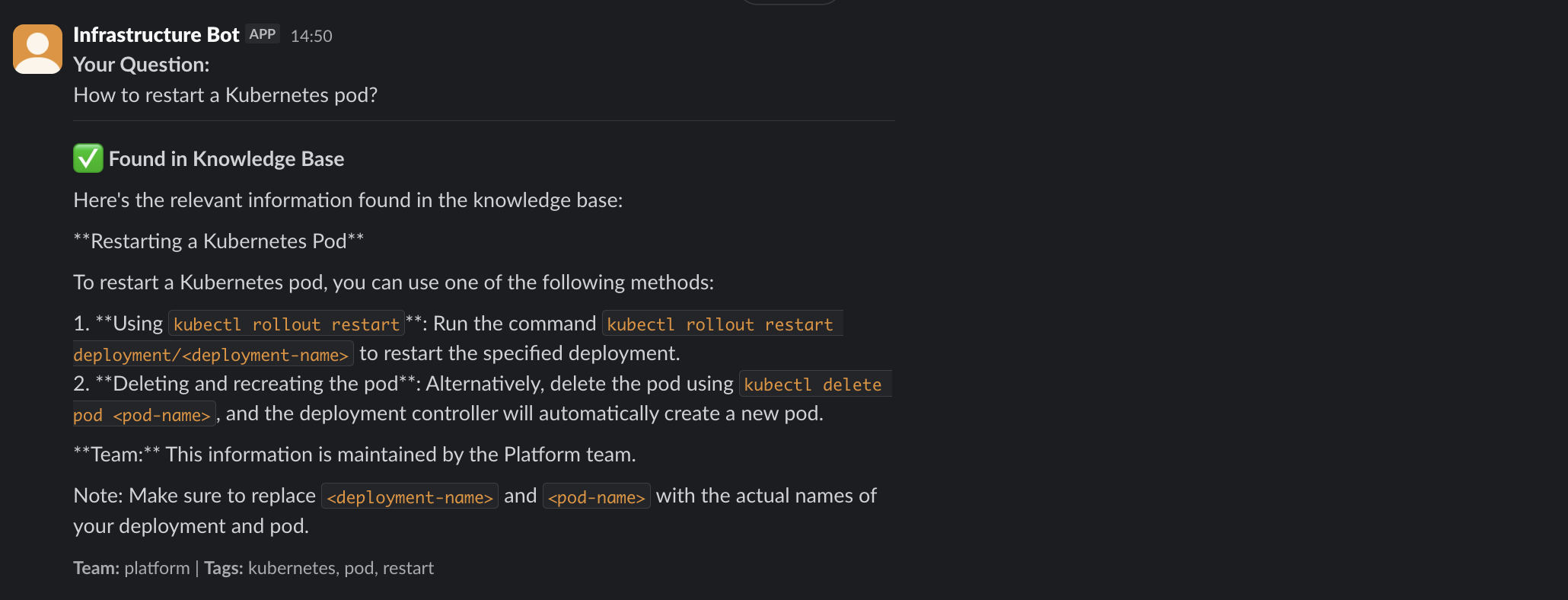
This reduces ticket volume significantly—common questions get answered in seconds without human intervention.
Smart Team Routing
When the bot can’t answer from the knowledge base, it creates a JIRA ticket and routes it to the appropriate team. It uses a two-tier approach: fast keyword matching, then AI classification.
Routing logic:
def route_to_team(question):
# Fast keyword matching
if 'kubernetes' in question or 'pod' in question:
return 'platform'
if 'database' in question or 'postgres' in question:
return 'database'
# Fallback to AI classification using LLM
team = llm.classify(
question,
teams=['platform', 'devops', 'database', 'security', 'network']
)
return team
What happens: The router checks for obvious keywords first (fast). If no match, it asks the LLM to classify the question based on team responsibilities.
Output:
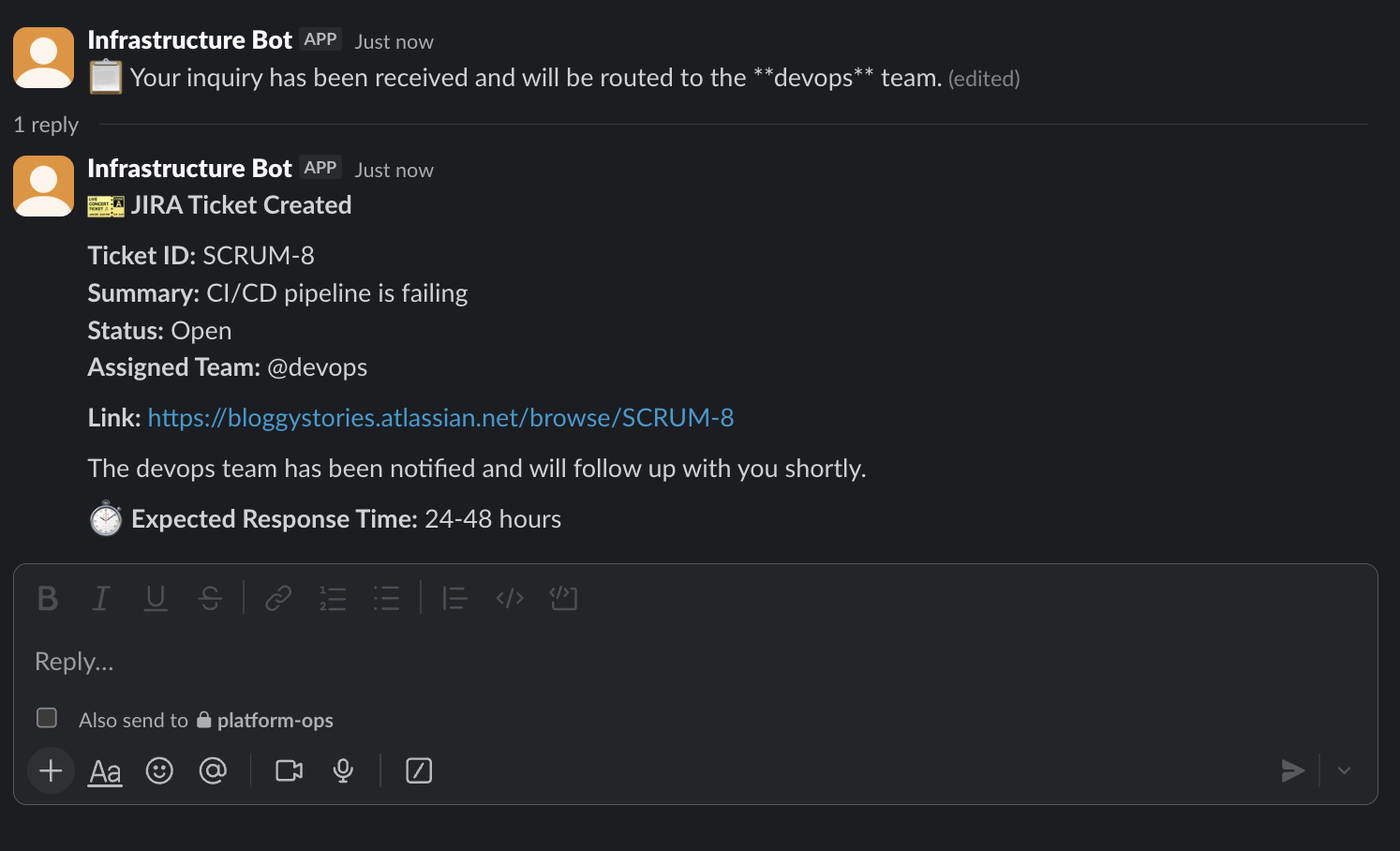
The ticket includes auto-generated summary, environment context, urgency classification, and team labels. The assigned team gets notified immediately.
JIRA Ticket Details:
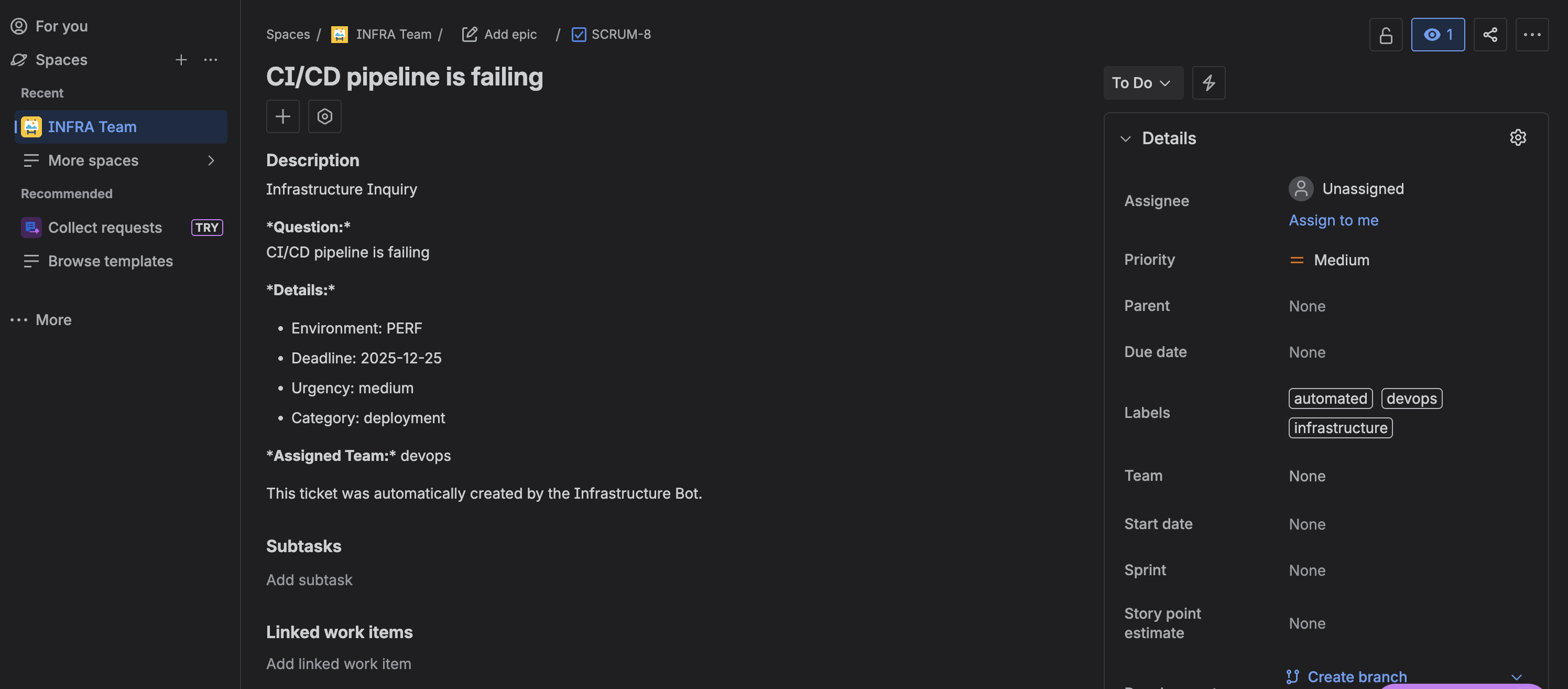
The ticket appears in JIRA with all fields properly populated: question, environment, deadline, urgency, category, and assigned team.
Architecture
The system uses three AI agents built with LangChain, each handling a specific task:
1. Supervisor Agent
- Orchestrates the entire workflow
- Classifies urgency (low/medium/high/critical)
- Decides: answer from KB or create ticket
2. Knowledge Agent
- Performs RAG search in vector database
- Filters by relevance threshold (strict <0.4 for high confidence)
- Synthesizes answer from retrieved documents
3. Router Agent
- Assigns tickets to correct team
- Uses keyword matching + LLM fallback
- Routes to: platform, devops, database, security, or network teams
Technology stack:
- Ollama - Local LLM deployment (
llama3.1:8bfor reasoning,nomic-embed-textfor embeddings) - ChromaDB - Vector database for semantic search
- PostgreSQL - Inquiry tracking and metrics
- Redis - Caches search results (reduces latency)
Metrics Dashboard
All inquiries are tracked in PostgreSQL with full metadata: question, environment, urgency, team assignment, KB resolution status, and JIRA ticket ID.
Output:
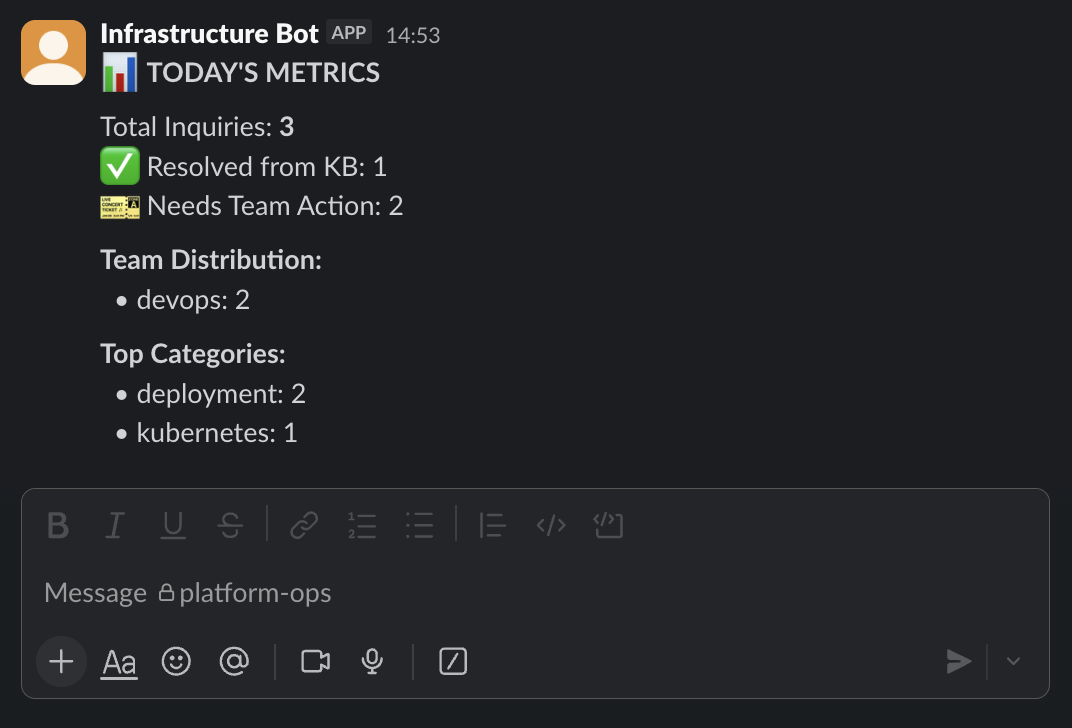
Key metrics:
- KB hit rate - % of questions answered without human intervention
- Team distribution - Workload balance across teams
- Category breakdown - Most common inquiry types (kubernetes, database, network, etc.)
Access via /infra-metrics command in Slack or run python metrics.py for detailed reports.
Quick Setup
1. Install Ollama and models
ollama pull llama3.1:8b
ollama pull nomic-embed-text
2. Start Docker services
docker-compose up -d
This starts PostgreSQL, Redis, and ChromaDB containers.
3. Configure environment
Create .env file with Slack tokens, JIRA credentials, and database settings.
4. Run the bot
python src/main.py
Bot connects to Slack and starts listening for /infra-inquiry commands.
Expected output:
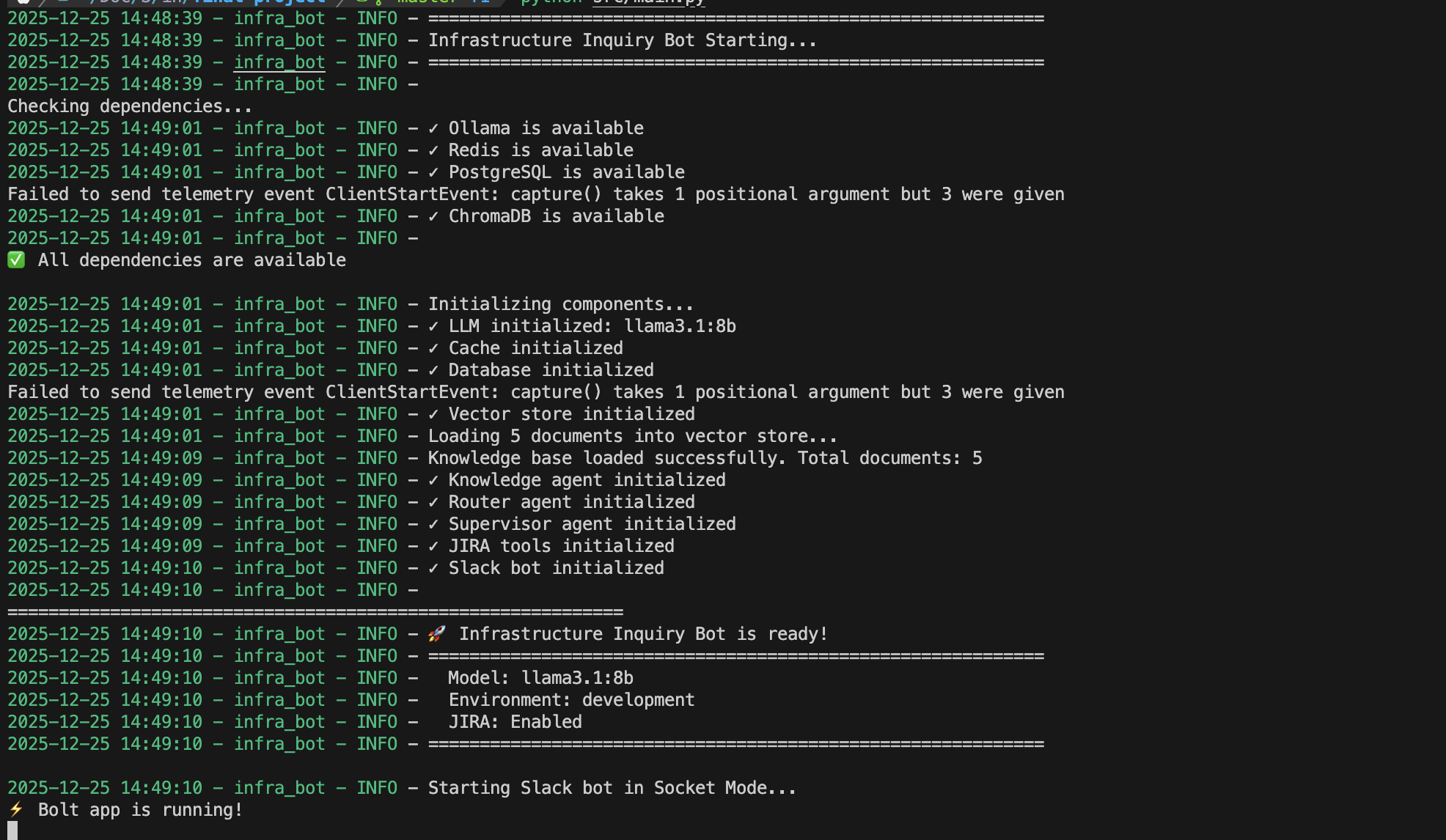
You’ll see all components initialize: Ollama connection, Redis cache, PostgreSQL database, ChromaDB vector store, AI agents (Supervisor, Knowledge, Router), and Slack bot in Socket Mode.
Conclusion
This bot reduces manual ticket creation and provides instant answers from a searchable knowledge base. All inquiries are tracked in PostgreSQL for continuous improvement of the knowledge base and team workload analysis.
Get the Full Source Code
📧 Enter your email to access the complete repository
Free • No spam • Unsubscribe anytime